Bookkeeping
Labor Efficiency Variance
The material quantity variance can yield unusual results, since it is based on a standard unit quantity that may not be even close to actual usage. The material quantity is usually set by the engineering department, and is based on an expected amount of material that should theoretically be used in the production process, along with an allowance for a reasonable amount of scrap. If the standard is excessively generous, there will be a long series of favorable material quantity variances, even though the production staff may not be doing an especially good job. Conversely, a parsimonious standard allows little room for error, so there is more likely to be a considerable number of unfavorable variances over time. Thus, the standard used to derive the variance is more likely to cause a favorable or unfavorable variance than any actions taken by the production staff. Angro Limited, a single product American company, employs a proper standard costing system.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
For example, regression analysis might reveal that a 10% increase in supplier lead time results in a 5% increase in material quantity variance. Armed with this knowledge, companies can focus their efforts on improving supplier lead times to achieve better cost control. Additionally, the use of variance decomposition allows businesses to break down complex variances into more manageable components, providing deeper insights into specific areas of concern. It’s important to note that direct material variance can be broken down into more specific components, such as price and quantity variances.
Get Your Questions Answered and Book a Free Call if Necessary
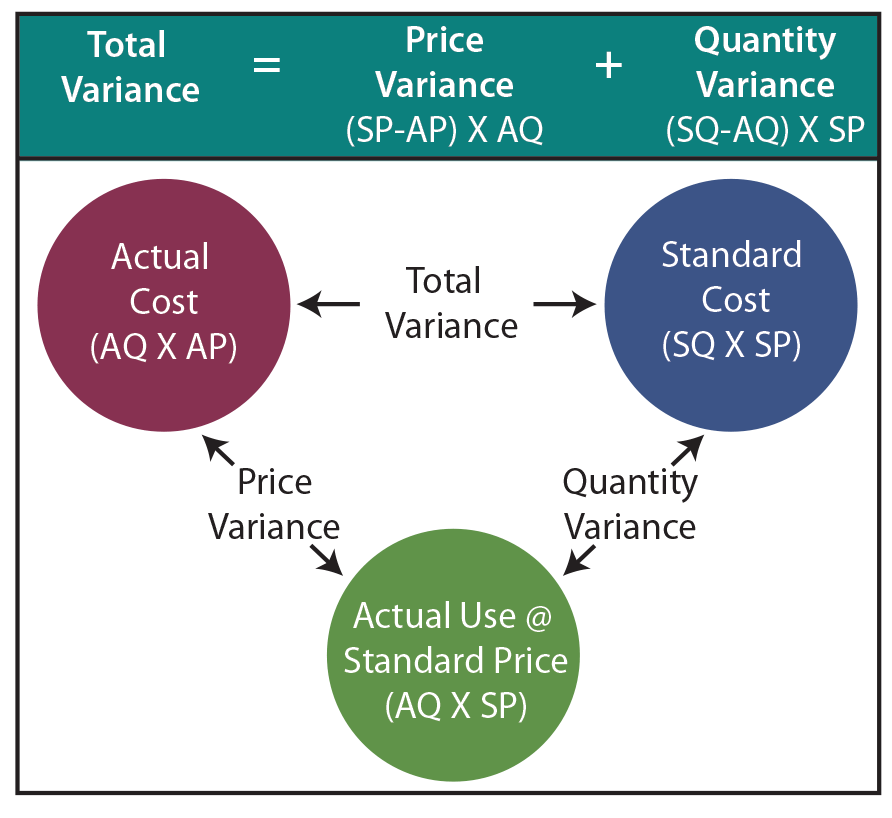
To begin with, calculating direct material variance involves comparing the standard cost of materials to the actual cost incurred. This comparison helps businesses understand whether they are spending more or less than anticipated on raw materials. The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process. The variance is calculated using the direct materials quantity variance formula, which takes the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity, and multiplies this by the standard price per unit of material.
Variance Analysis Accounting Journals
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable economic order quantity eoq and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Calculator for Direct Material Price Variance
- Total actual and standard direct materials costs are calculated by multiplying quantity by price, and the results are shown in the last row of the first two columns.
- Direct material price variance is a key metric in cost accounting that measures the difference between the actual cost incurred for purchasing direct materials and the standard cost that was expected or budgeted for those materials.
- Similarly, if a material quantity variance is found, a thorough review of the production process, employee performance, and equipment efficiency is necessary.
The difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production is known as Direct Material Cost Variance. Materials price variance (or direct materials price variance) is the part of materials cost variance that is attributable to the difference between the actual price paid and the standard price specified for direct materials. Premium Furniture, a US based Inc., uses a standard costing system to control its direct materials and conversion costs. During the month of December 2022, its workers used 3,750 feet of timber to finish 1,500 office chairs. The standard length of timber allowed to manufacture an office chair is 2.75 feet and the standard rate per foot of timber is $3.50. How much is the direct materials quantity variance of Prime Furniture Inc. for the month of December 2022?
Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction. In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured. Lumber costs may rise due to increased fuel costs and then lower when diesel prices stabilize.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. If the balance is considered insignificant in relation to the size of the business, then it can simply be transferred to the cost of goods sold account. Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University. He has taught accounting at the college level for 17 years and runs the Accountinator website at , which gives practical accounting advice to entrepreneurs. This formula is critical for understanding how actual spending tracks against estimations.
The standard cost of actual quantity purchased is calculated by multiplying the standard price with the actual quantity. This amount will represent the expected expenditure on direct material for this many units. The difference between this actual expenditure and the actual expenditure on direct material is the direct materials price variance.
A material quantity variance is the difference between the actual amount of materials used in the production process and the amount that was expected to be used. The measurement is employed to determine the efficiency of a production process in converting raw materials into finished goods. Material quantity variance is favorable if the actual quantity of materials used in manufacturing during a period is lower than the standard quantity that was expected for that level of output. Where,SQ is the standard quantity allowed,AQ is the actual quantity of direct material used, andSP is the standard price per unit of direct material. Another advanced technique is the application of statistical methods, such as regression analysis, to understand the relationship between different variables affecting material costs. By analyzing historical data, businesses can identify key drivers of variances and quantify their impact.
By understanding these trends, companies can anticipate future variances and take proactive measures to mitigate them. Analyzing direct material variance is a powerful tool for businesses aiming to maintain cost control and enhance profitability. By delving into the specifics of variances, companies can uncover inefficiencies and make informed decisions to optimize their operations.